The value of Bitcoin (BTC), unlike traditional fiat currencies such as the Euro or the U.S. Dollar, is not determined by a centralized authority like a central bank. Instead, Bitcoin’s price is determined based on supply and demand. Bitcoin has a supply cap where no more than 21 million BTC will ever exist. Bitcoin’s price increases when demand exceeds supply and decreases when demand falls. Other factors such as the cost of producing bitcoin through mining, regulations, news, and competition from other cryptocurrencies can influence the supply and demand and thus, influence the bitcoin’s price.
The price volatility of Bitcoin has left many skeptics questioning the mathematical and economic basis of price movements while searching for a generalized justification for its valuation. Since Bitcoin is decentralized, it doesn’t follow the monetary policy of governments, and Bitcoin is not backed by any underlying asset or government. This creates skepticism among investors and consumers who appreciate the price stability signals a fiat currency enjoys from government policy and support.
Supply and Demand for Bitcoin
The price of Bitcoin is determined in the same way that the value of the U.S. dollar is determined: supply and demand. Like fiat currency, when the demand for bitcoin increases, the price increases. When demand for bitcoin falls, the price falls.
It is reasonable to assert that factors that increase the utility of bitcoin, increase the price of bitcoin directly or indirectly. For instance, the Lightning Network enables bitcoin to be used as a medium of exchange in commerce. This has had a positive impact on Bitcoin’s adoption and thus increases demand for bitcoin, generally.
➤ Learn more about about how people use bitcoin in commerce today.
On the supply side, Bitcoin is a unique asset in that its new supply schedule is absolutely inelastic; it is completely immune to fluctuations in demand. When most goods, including fiat currency and gold, experience a rise in demand, producers react by increasing production and returning prices to an equilibrium. When demand for bitcoin rises, thanks to the difficulty adjustment, the production of new bitcoin does not rise.
Stock-to-Flow
The stock-to-flow (S2F) model is commonly used to analyze the impact of scarcity on the price of an asset. The stock-to-flow ratio is a number that indicates how many years it will take to produce the current stock at the current production rate. Essentially, the stock-to-flow ratio is the inverse of the inflation rate of an asset. According to the stock-to-flow model, a higher stock-to-flow ratio should yield a higher price.
➤ Learn more about the Stock-to-Flow model.
Every four years, the Bitcoin halving cuts the block subsidy in half, reducing the flow of new bitcoin into the market, thereby increasing the stock-to-flow ratio and making Bitcoin even more scarce. If the stock-to-flow model is applied to Bitcoin, this should trigger a rise in price, and indeed, each past halving has triggered a dramatic price rise in the following months. However, whether these price appreciations validate the stock-to-flow model is still a topic of much disagreement.
➤ Learn more about the Bitcoin Halving.
How Does Bitcoin’s Scarcity Influence Price?
Bitcoin’s scarcity significantly impacts its price, largely because there is a hard cap on the total amount that will ever exist—only 21 million bitcoins. Unlike fiat currencies, which central banks can print indefinitely, Bitcoin’s supply is fixed. This scarcity is reinforced by the way new bitcoins are created through the mining process, which is designed to slow down production over time through the halving. As a result, as demand for Bitcoin increases, the limited supply exerts upward pressure on its price.
Bitcoin’s monetary policy is transparent and predictable since everyone knows exactly how many bitcoin are currently available and what will be the maximum that will ever be created. This transparency gives investors confidence, knowing that bitcoin’s value cannot be diluted by unexpected increases in supply. This known scarcity and predictability make Bitcoin a compelling option for investors looking to protect their wealth from inflation or monetary debasement, where traditional currencies might lose value over time.
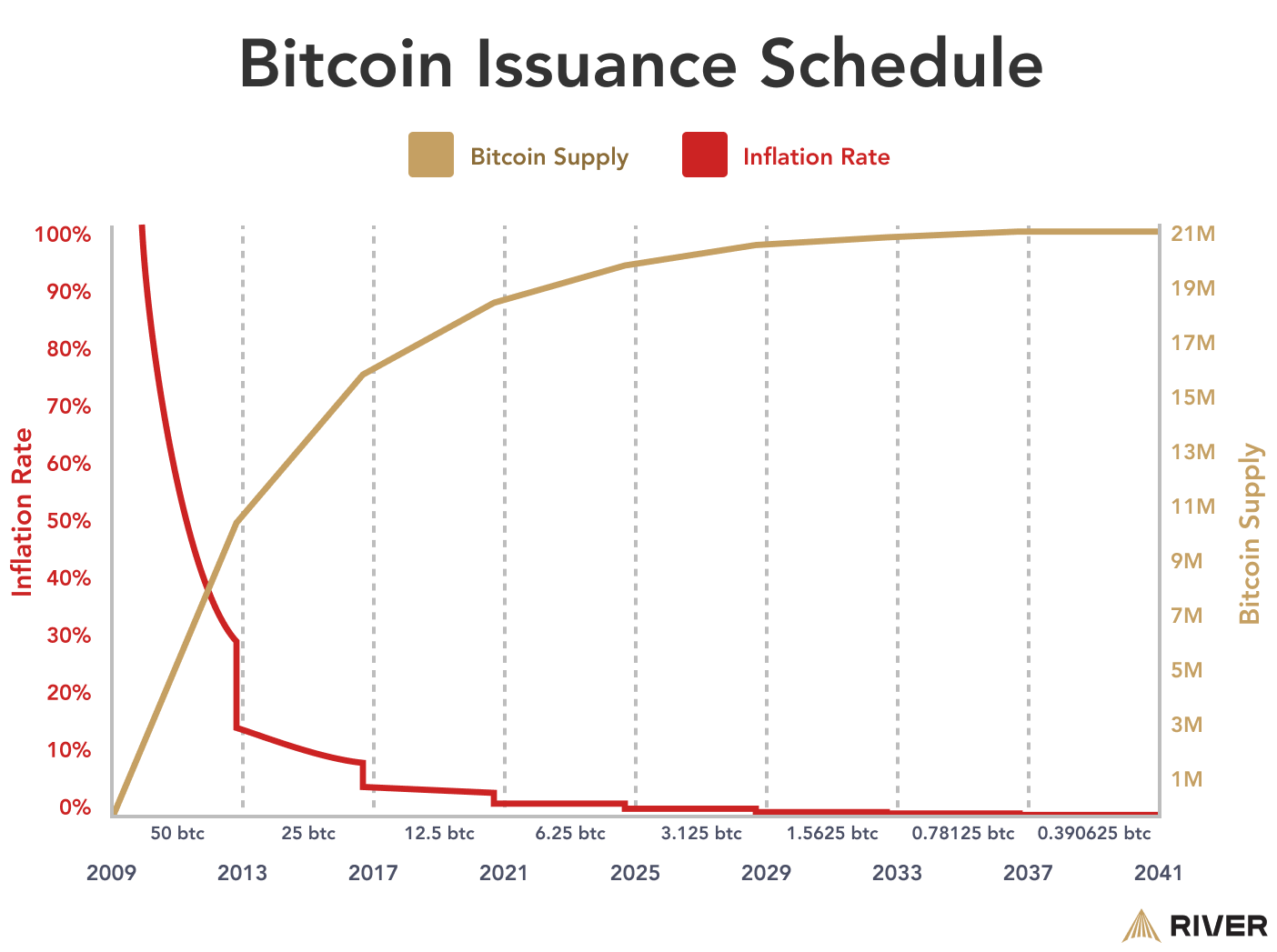
Comparatively, the creation and distribution of fiat currency is potentially infinite and unpredictable. Most central banks target a relatively low inflation rate, but these rates are subject to change by a small committee at any time, and the true inflation rate of fiat currencies is nearly impossible to measure. For example, the Federal Reserve is targeting a 2% inflation rate, even though the true rate is significantly higher.
Thanks to a finite supply and a relatively small market cap, the price of Bitcoin is also much more sensitive to changes in demand, resulting in increased price volatility.
➤ Learn more about the impact of Bitcoin’s finite supply.
Inflation and Deflation
Inflation occurs when the money supply or the velocity of money increases rapidly, causing prices to rise and reducing the value of currency. Bitcoin is deflationary due to its finite supply. The finite supply protects bitcoin from hyperinflation. A government’s ability to print an unlimited amount of currency has caused periods of hyperinflation that have driven the value of many fiat currencies, including the German Mark and Zimbabwean dollar, down to zero.
➤ Learn more about about Zimbabwe, Germany and Hyperinflation.
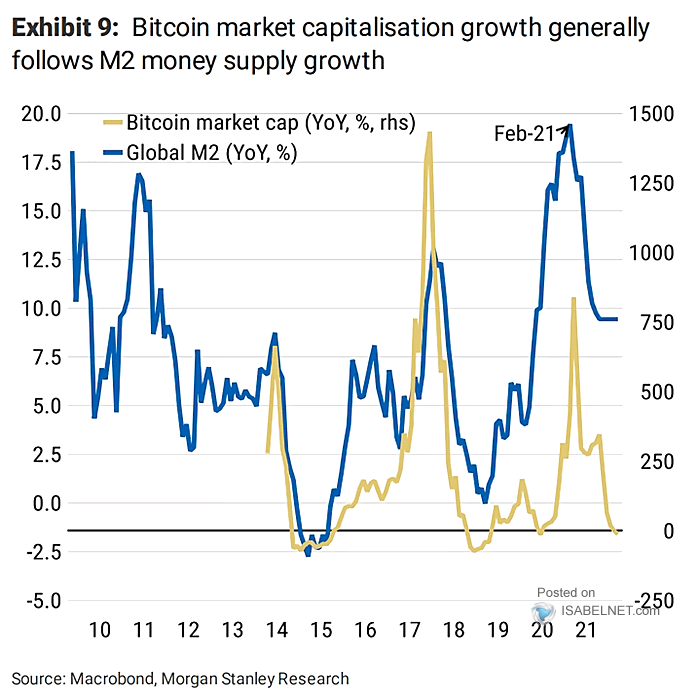
Based on available economic data, bitcoin’s price appears to be influenced by the availability of liquidity in global capital markets. When there is more money available, price tends to increase, generally speaking.
Concerns over deflationary spirals are not well-founded or supported by economists; supply and demand have always corrected deflationary events in bitcoin and fiat currency. A finite supply also makes Bitcoin a secure long-term store of value, comparable and in some cases more advantageous than gold.
➤ Learn more about why Bitcoin has value.
Key Takeaways
- The Bitcoin price is determined through supply and demand.
- A finite supply of bitcoin mitigates inflation and deflation risks.
- The stock-to-flow model uses the current circulation of bitcoin and the rate of production to measure the effect of scarcity on the BTC price.


