Bitcoin, unlike traditional fiat currencies, is not backed by a physical commodity like gold or silver, nor by the promise of a government or central bank. Bitcoin’s value comes from the widespread trust in its security, scarcity, and predictability. Similar to gold, Bitcoin is sound money and does not require backing because inherent properties that allow it to be a good store of value, medium of exchange, and unit of account.
Watch the video below to understand why Bitcoin has value.
Bitcoin is enabled by various factors such as mathematics and cryptography that lay the foundation of a monetary system that is borderless, permissionless, and censorship-resistant.
The cryptographic algorithms used by Bitcoin play a crucial role in securing transactions and maintaining the integrity of the ledger. These algorithms make transactions secure, verifiable, and immutable.
Bitcoin Halving and Supply Scarcity
A key characteristic that adds to Bitcoin’s value is its fixed supply limit of 21 million coins. This inherent scarcity, coupled with a predictable and decreasing rate of new coin issuance, gives a deflationary aspect that can drive value over time.
The Bitcoin Halving ensures its fixed supply scarcity by slowing down the rate at which new bitcoin is created. Bitcoin’s low inflation rate is trending towards zero.
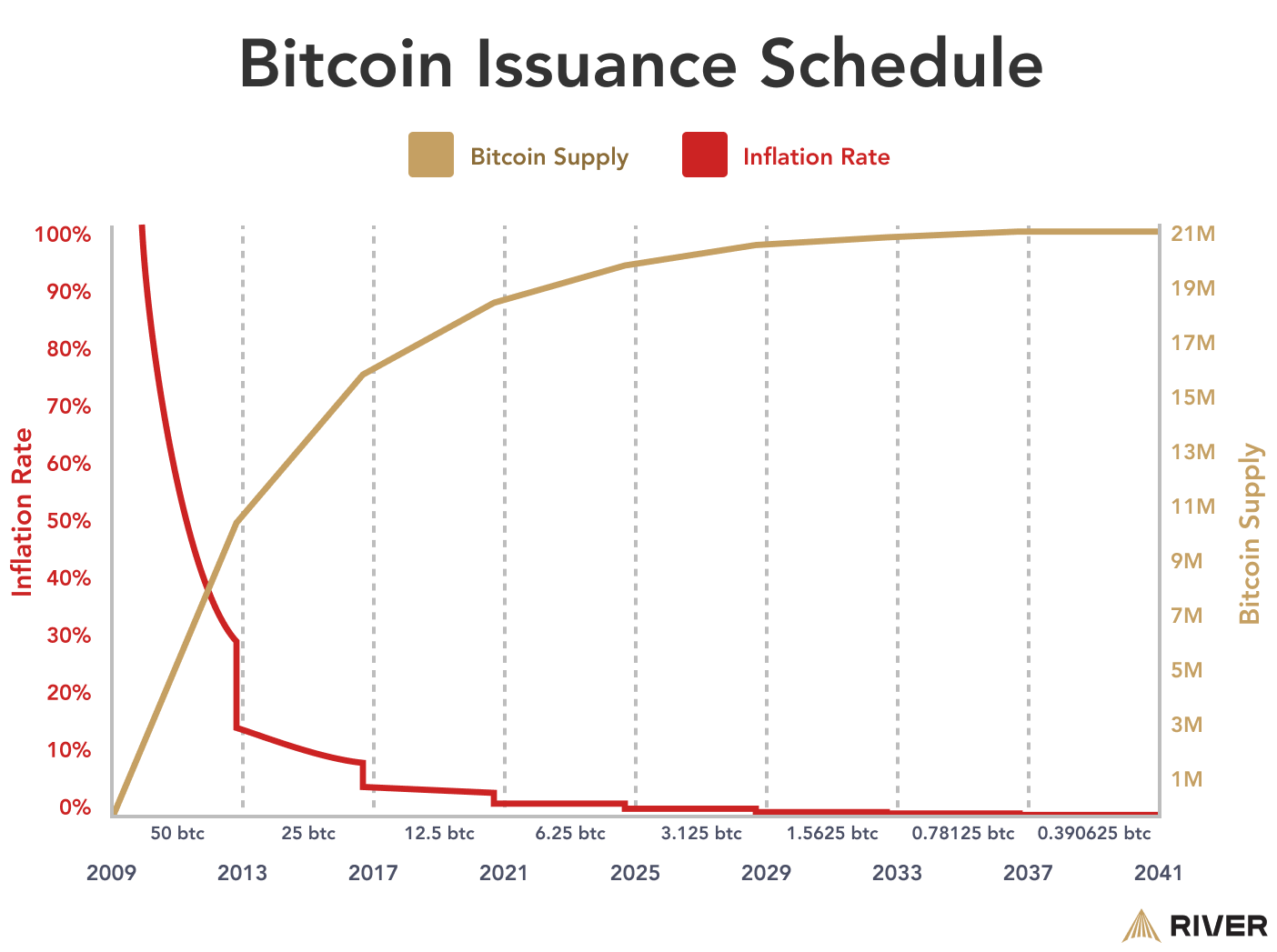
Bitcoin’s growing community of users, developers, businesses, and investors also supports its value. The widespread adoption and acceptance of Bitcoin as a form of payment and store of value contribute to its overall worth. Market demand and investor sentiment play significant roles in influencing Bitcoin’s price, which fluctuates based on supply and demand dynamics.
These factors collectively support Bitcoin’s value and functionality, setting it apart from traditional currencies and commodities.
The lack of backing does not mean Bitcoin does not have value. The majority of currencies used in the global economy do not have any backing. By definition, a fiat currency is a currency without backing, and this is what every major economy in the world uses to conduct daily transactions.
➤ Learn more about fiat currencies.
However, a government-issued currency usually derives its stability from the central bank’s control of the quantity of money issued, as well as the faith its citizens and other nations place in the government’s stability. When this faith is eroded, a fiat currency can depreciate rapidly as citizens and foreign nations try to trade their currency for more stable assets.
Bitcoin as Digital Gold
For a better comparison to Bitcoin, we must look at assets that are not issued by a central authority. Precious metals, like gold, that derive their value from scarcity instead of construction and engineering uses are similar to Bitcoin in this sense.
An ounce of gold doesn’t entitle you to exchange it for another valuable asset. Instead, the gold is valuable because the gold itself is valuable. Individuals are generally not worried about their gold becoming worthless because the market has established that gold has value for thousands of years. Similarly, Bitcoin’s value comes from the demand for Bitcoin and does not require any backing to maintain this value.
➤ Learn more about why Bitcoin has value.
What Is a Backed Currency?
A backed currency is a form of currency that comes with a guarantee that it can always be exchanged for a predetermined amount of another asset. For example, a currency backed by gold may have a guarantee that 100 units of the currency can be traded for an ounce of gold.
The most common assets to back a currency with are gold and silver, but a currency can be backed by anything. Starting in 1879, the U.S. dollar was backed by gold, largely due to gold’s fungibility and scarcity, important characteristics of money.
➤ Learn more about money’s characteristics.
A currency can also be backed by another currency. This is known as a pegged currency. By backing a currency, you guarantee that it will always be worth at least as much as it can be traded in for. However, backed currencies can easily lose their credibility if citizens lose faith in the government’s ability to maintain the fixed exchange rate. In this case, black markets for currency exchanges arise, allowing the real exchange rate to emerge.
Why Are Currencies Backed?
Currencies are backed to ensure that they maintain their value. Currency is a necessary tool for running a government, but many governments have faced unstable currencies. This makes it difficult for citizens to use the currency effectively and hurts economic growth. A government can print its currency indefinitely, but the more it prints the less scarce the currency becomes, resulting in inflation. A backed currency can be protected from inflation, but the government will need to acquire more of the backing asset in order to maintain a credible backing.
To combat unstable currencies, a government can back their currency with another asset to reassure citizens that it will retain its value. However, this method will only succeed if citizens trust the promise of the backing.
If holders of the currency begin to doubt that the government has enough of the backing asset to ensure the promised exchange rate, then the currency may deteriorate in value rapidly as individuals attempt to exchange their currency for the scarce underlying asset.
Key Takeaways
- Backing a currency is done by the currency’s issuer to ensure its value.
- Bitcoin, gold, and fiat currencies are not backed by any other asset.
- Bitcoin has value despite no backing because it has properties of sound money.


