While many investors look to buy bitcoin in anticipation of its price increasing, other investors look to profit from bitcoin falling in price. The strategy to profit from a decline in bitcoin’s price is called shorting or short selling. In this article, we provide an overview of the different ways to short bitcoin and highlight the risks involved.
Can You Short Bitcoin?
Bitcoin can be shorted through a variety of direct and indirect methods including margin trading, derivatives, and bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Short selling, or “shorting” bitcoin allows investors to profit from price declines. As Bitcoin gains prominence in mainstream finance, the number of ways to short bitcoin has increased.
What Is Short Selling Bitcoin?
Short selling bitcoin is an investment strategy that allows investors to profit from the decline in bitcoin’s price. Shorting involves borrowing bitcoin when its price is high, selling it immediately at the current market price, and then buying it back later at a lower price. To close the short trade, the investor returns the borrowed bitcoin and pockets the price difference as profit.
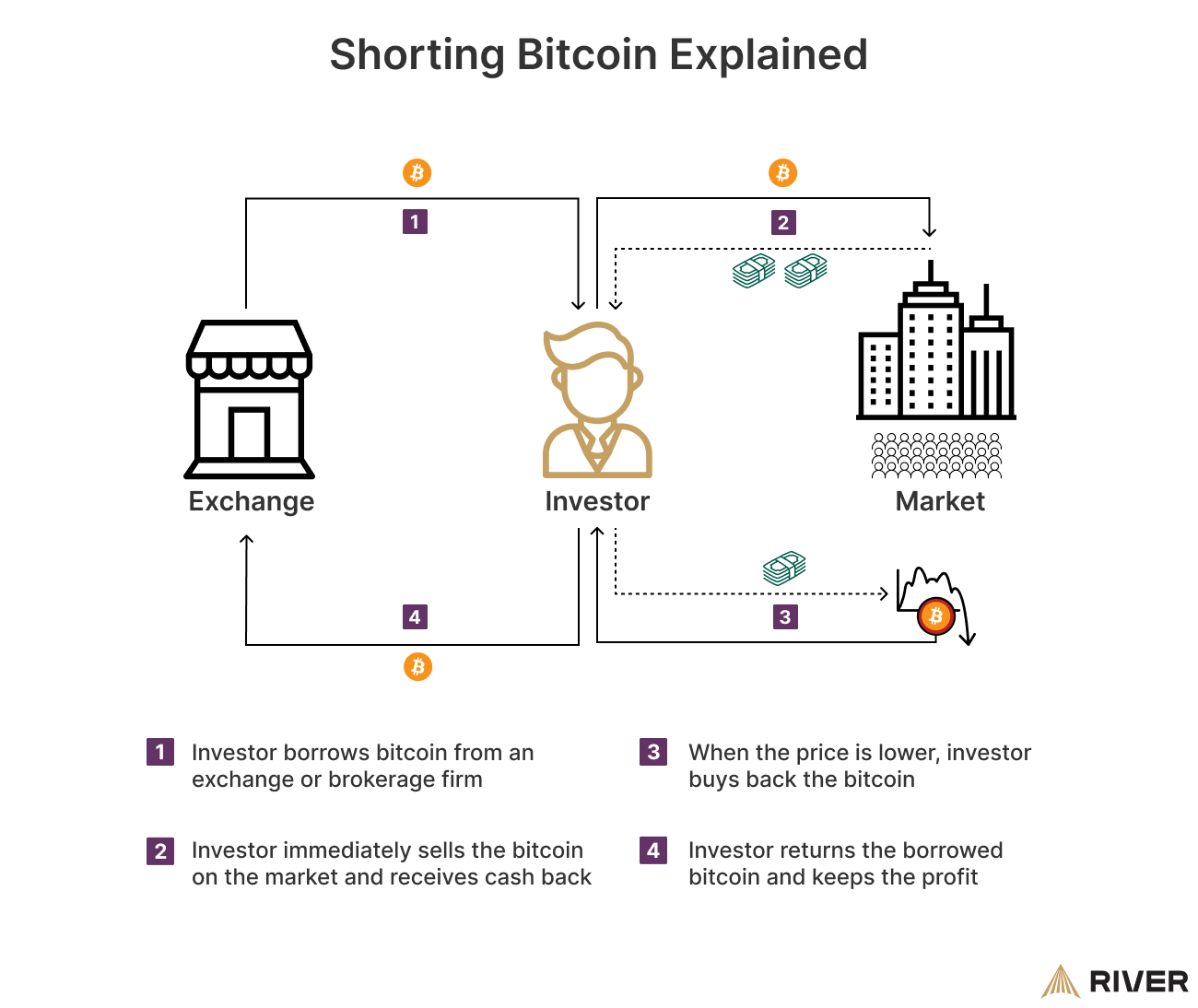
➤ Learn more about Why Does Bitcoin Have Value?
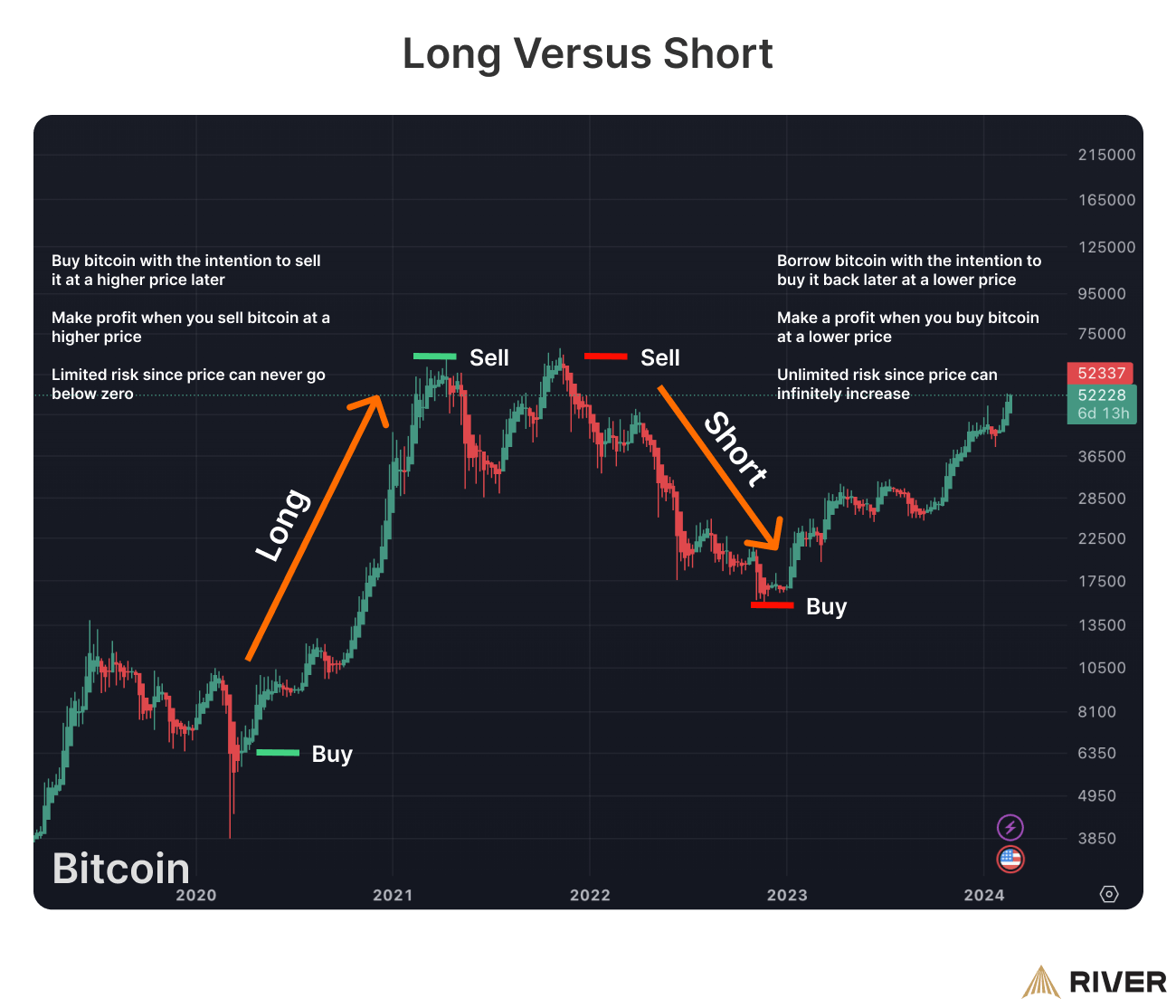
Long Position Versus Short Position
“Long” and “short” positions represent two fundamental trades that investors can take when they trade securities or commodities like bitcoin. Taking a long position means buying bitcoin with the expectation that its price will rise. Conversely, a short position involves borrowing bitcoin to sell at the current price, hoping to repurchase it cheaper if the price falls. Both strategies are speculative and reflect different outlooks on bitcoin’s future price movements.
Can You Make Money Shorting Bitcoin?
In theory, short selling bitcoin can be as profitable as taking long positions. For example, if you short sell and the price of bitcoin falls by $10,000, your profit could be the equivalent to what you would have earned from a long position if the market had increased by $10,000. However, shorting bitcoin carries tremendous risk as outlined below.
What Are the Risks of Shorting Bitcoin?
Shorting bitcoin comes with risk as the asset is relatively volatile in fiat terms due to its short history — it has been around for only 14 years. Price swings can happen often, leading to substantial losses, especially when leverage is involved. If bitcoin’s price rises instead of falling, the short seller will be forced to buy back the bitcoin at a higher price, leading to potentially unlimited losses since there is no limit on how high bitcoin’s price can go.
➤ Learn more about Why Bitcoin’s Price Is Volatile?
For example, if you buy bitcoin at $50,000, the lowest it can fall to is $0. However, if you short bitcoin at $50,000, the price can rise infinitely to $100,000 and beyond. To close the short position, the investor must return the borrowed bitcoin no matter the price, resulting in an unlimited downside.
What Is a Short Squeeze?
A short squeeze is when bitcoin’s price rises, and short sellers rush to buy back the bitcoin to limit their losses. This creates buying pressure, which can drive the price up even further, leading to even more short sellers covering their positions and causing a rapid price increase. This situation can result in massive losses for short sellers and illustrates the high-risk nature of short selling.
How To Short Bitcoin: 8 Different Ways
1. Shorting Bitcoin With Margin Trading
One of the most common ways to short bitcoin is through margin trading. Margin trading allows investors to borrow money to make a trade. In other words, margin means utilizing leverage, which can amplify profits or losses.
Leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 2:1, 5:1, 10:1. For example, with a 10:1 leverage, you can place a trade worth 10 times the amount of your own capital. If you have 1 BTC in capital, you could potentially trade with 10 BTC by borrowing the additional funds.
➤ Learn more about Leveraged Bitcoin Trading
2. Short Selling Bitcoin Assets
This method involves selling bitcoin at a high price and repurchasing it when the price drops. This approach to short selling bitcoin is accessible for beginners, eliminating the necessity to familiarize oneself with trading platforms. Additionally, it carries a lower risk, as the potential loss is limited to the amount you invest.
3. Shorting Bitcoin With Futures Contracts
Bitcoin futures are financial contracts that bind you to buy or sell bitcoin at a predetermined price on a specific future date. Shorting bitcoin through futures involves selling these contracts with the expectation that bitcoin’s price will drop. You can trade bitcoin futures at the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and TD Ameritrade.
4. Shorting Bitcoin With Options Contracts
Options give you the right, but not the obligation, to sell bitcoin at a specific price, offering a way to manage risk. Options are different from futures in that you are not obligated to execute the contract so investors can limit their losses. For example, a popular exchanges to trade bitcoin options is Deribit.
5. Shorting Bitcoin With Inverse Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
Bitcoin inverse ETFs or short bitcoin ETFs are financial instruments designed to provide returns that are inversely correlated to the performance of bitcoin. This means that if the price of bitcoin falls, the price of the inverse ETF is expected to go up, and vice versa. These ETFs achieve this inverse performance through the use of financial derivatives such as futures contracts, options, and swaps. For example, the ProShares Short Bitcoin Strategy ETF (BITI) is an inverse bitcoin ETF.
➤ Learn more about What Is a Bitcoin ETF
6. Shorting Bitcoin With Bitcoin Stocks
Short selling bitcoin-related stocks or companies with significant exposure to bitcoin is an indirect way to short bitcoin. For example, MicroStrategy, a business intelligence company, has made substantial investments in bitcoin, making its stock price increasingly correlated with the price movements of bitcoin.
➤ Learn more about how much bitcoin MicroStrategy owns and who the top bitcoin holders are in 2024
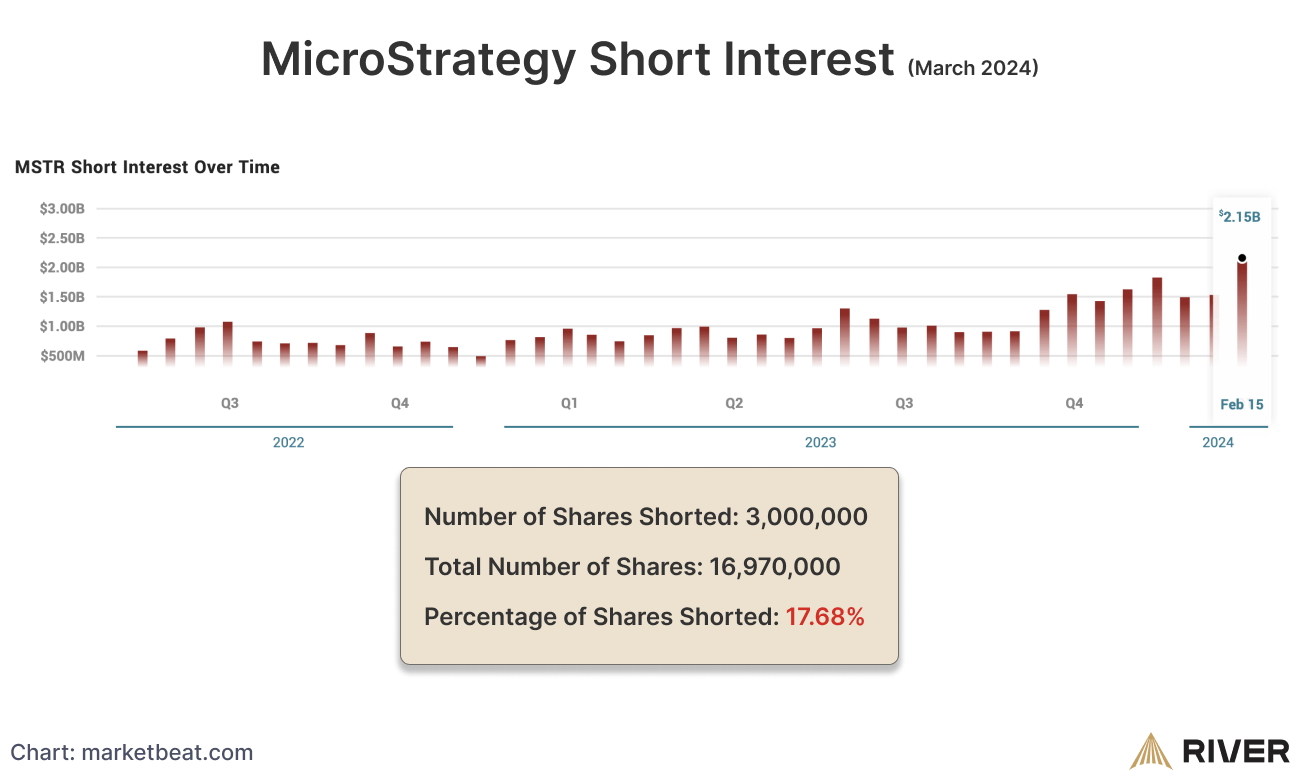
About 17.68% of MicroStrategy’s shares are shorted. Some other bitcoin-related stocks are Marathon Digital Holdings and Riot Platforms Inc.
7. Shorting Bitcoin With Prediction Markets
Prediction markets are markets where you speculate on the outcome of events. Cryptocurrency prediction markets are relatively new, but do present an opportunity to short bitcoin.
8. Shorting Bitcoin With Contracts for Difference (CFDs)
A contract for difference (CFD) is a financial product where investors get paid out based on the price difference between open and closing prices. CFDs are similar to bitcoin futures, but have more flexible expiry dates. There are only a handful of brokers that offer CFDs. Shorting bitcoin through CFDs involves opening a contract that will pay the difference between the opening and closing prices if the price of bitcoin falls.
Shorting Bitcoin as a Hedge
Investors short bitcoin as part of a hedge in their investment strategy. Due to the often unpredictable nature of the bitcoin market, shorting serves as a strategy for investors to safeguard themselves against potential losses in their other trading positions. For example, a trader who purchases bitcoin in the spot market may choose to short bitcoin via derivatives such as option contracts.
The Costs of Shorting Bitcoin
Shorting bitcoin often involves certain costs and fees, which can vary significantly from one platform to another.
- Transaction Fees: Fees on exchanges can sometimes be categorized into maker and taker fees, which depend on whether the transaction adds or subtracts liquidity. Fees can also vary from spot markets and derivative markets like futures and options.
- Borrowing Costs: When short selling bitcoin, investors must borrow BTC, which can incur margin fees. These fees are based on a variable daily rate that adjusts in response to the market.
- Miscellaneous Fees: Exchanges sometimes charge post-trade fees and charge an additional fee if your position gets liquidated.
Conclusion
It’s essential to approach short selling with caution and thorough research. Understanding the different methods to short bitcoin and being aware of the associated risks can help investors make informed decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Shorting bitcoin presents an opportunity for investors who believe that the price of bitcoin will fall.
- Short selling bitcoin carries significant risks due to its volatility, with methods like margin trading amplifying potential profits and losses through leverage.
- There are various direct and indirect ways to short bitcoin, including futures, options, inverse ETFs, and bitcoin-related stocks, each requiring an understanding of market risks and strategies to manage potential losses.


