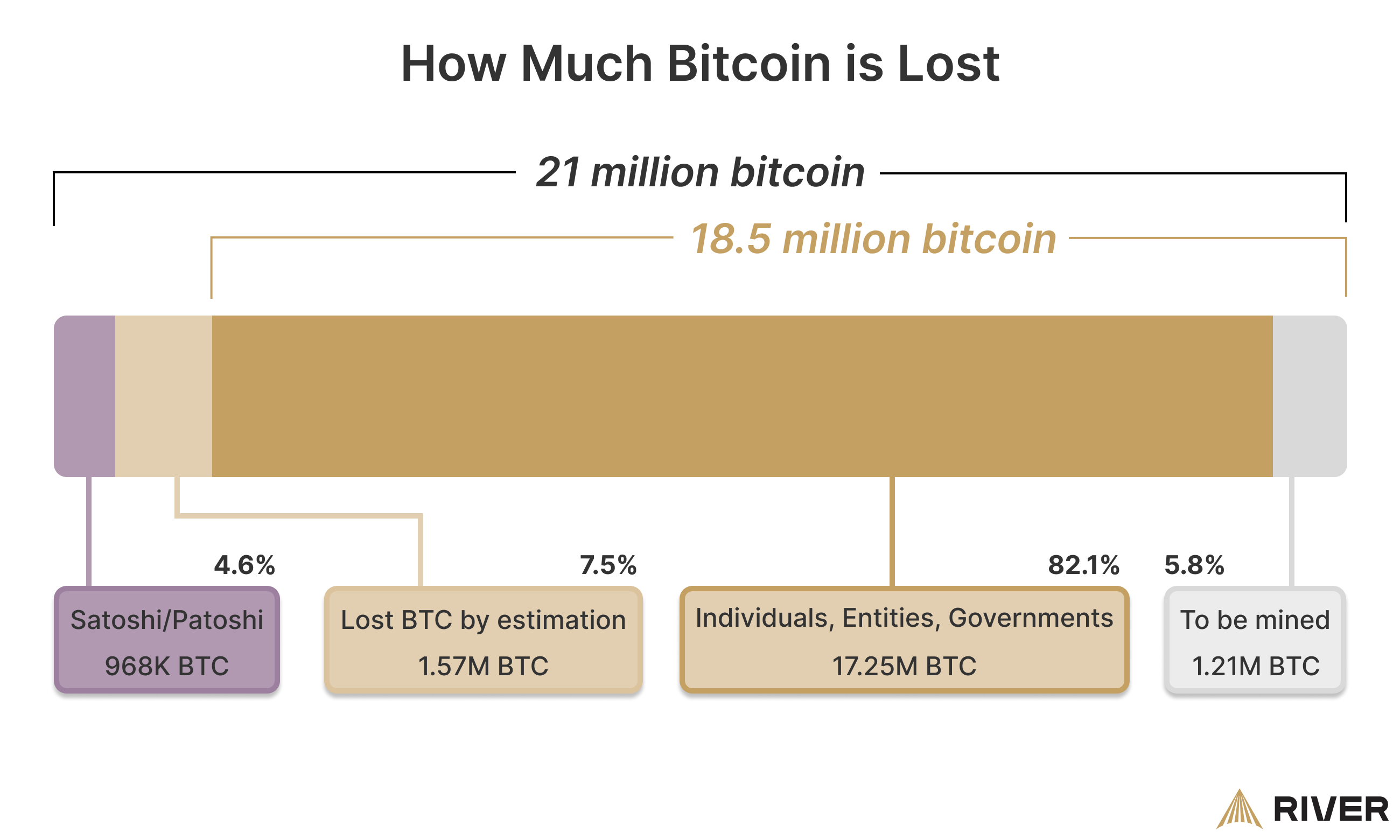
When Bitcoin is lost, it essentially becomes irretrievable and permanently unspendable. The blockchain records the bitcoin as still existing at a certain address, but without the private key, it cannot be moved or spent. This creates a situation where the bitcoin is still “there,” but effectively gone forever. Once bitcoin is lost, it reduces the total supply of spendable bitcoin, making the remaining bitcoin slightly more scarce. Currently, it is estimated that roughly 1.57 million bitcoin are lost.
When is Bitcoin Considered “Lost”?
Bitcoin is considered lost when it can no longer be spent by anyone. Bitcoin is controlled by private keys, much like physical keys control money in a safe or vault. Private keys create signatures, which are required to spend bitcoin. Without the private key, no signature can be created, and all funds linked to that key are unusable. The simplest way to avoid losing bitcoin is to safeguard private keys.
How Much Bitcoin Is Lost?
There is no way to know exactly how many bitcoin are lost forever. In Bitcoin’s early days, people did not realize its future value, resulting in many unfortunate losses, thefts, and mistaken transactions. We estimate that roughly 1.57 million bitcoin are lost, lowering the hard cap from 21 million to 19-20 million. If you assume that Satoshi’s bitcoin will be forever dormant, then the hard cap drops to about 18 million BTC.
How Is Bitcoin Lost?
The Bitcoin blockchain is an immutable ledger, which means that all bitcoin transactions are final, and thus making mistakes in transactions can be very unforgiving. Humans are the sole cause of lost bitcoin, not Bitcoin or the blockchain technology.
➤ Learn more about choosing a Bitcoin wallet
Millions of bitcoin have not moved addresses for a significant period of time, and the market is uncertain whether they will re-enter circulation. However, this does not automatically mean they are lost.
One famous example of unmoved bitcoin is the large cache of bitcoin held by Satoshi Nakamoto. No one is certain what Satoshi did with the private keys to their bitcoin, or whether the keys still exist, but the bitcoin has not moved since their creation.
— Satoshi Nakamoto explaining how lost coins affected the network positively in 2010.
By removing those coins from circulation, Satoshi reduced the total bitcoin supply by roughly 1 million. When bitcoin remains unmoved for a long period of time, the market responds as though the bitcoin has been removed from circulation and adjusts the price based on the lower supply.
Ways to Lose a Bitcoin Wallet
Bitcoin is a unique asset because it can be easily self-custodied without a trusted third party. However, self-custody places the responsibility of security and the risk of loss on the user; if a user takes full self-custody of their bitcoin and loses the private keys, the bitcoin is irreversibly lost.
➤ Learn more about how to get started with self-custody.
There are many available methods to self-custody bitcoin, but private keys held in self-custody on a personal hard-drive or other external storage device can accidentally be discarded or overwritten by new files; James Howells is infamous for having accidentally thrown out a hard-drive that would be worth nearly $300 million today.
A helpful way to keep a bitcoin wallet safe is to use a mnemonic phrase as a backup. A mnemonic phrase allows a wallet to be recreated even if the device used to access the wallet is lost or broken.
Third-party Security Risks
The Bitcoin community uses the generally accepted notion, “Not your keys, not your coins,” to illustrate the critical importance of private key control. Hackers have targeted exchanges on numerous occasions to obtain private keys and self-storage is prone to human error.
Custodians are typically institutions with experience and expertise in custody, making them more secure than exchanges and more reliable than self-storage.
➤ Learn more about bitcoin custody.
Mistaken Transactions
Bitcoin transactions are irreversible once they have been added to the blockchain.
Therefore, if a Bitcoin transaction sends bitcoin to an incorrect address, they are likely impossible to recover. The only way to recover bitcoin sent to an incorrect address is for the owner of that address to refund the mistaken transaction.
➤ Learn more about how bitcoin transactions work.
Luckily, this type of mistake is exceedingly rare, because many wallets check whether an address is valid before allowing a user to send bitcoin. The best way to avoid losing bitcoin through a mistaken transaction is to verify the address of a counterparty before transacting on-chain.
Inadequate Estate Planning
Bitcoin can be lost when a bitcoin owner passes away without sharing their private key or ensuring their private key can be recovered by an intended recipient.
In some cases, the deceased never revealed that they owned bitcoin during their lifetime, and their beneficiaries may be unaware there is bitcoin to be recovered. Similarly, many estate planning lawyers are unfamiliar with Bitcoin and do not know how to handle their deceased clients’ private keys with the appropriate level of care. If that happens, the bitcoin can be lost forever.
➤ Learn more about bitcoin estate planning.
How Can I Recover Lost Bitcoin?
There is no way to recover bitcoin that is truly lost. Some mistaken transactions have been refunded, but only when the counterparty personally knows the sender, which is infrequent. If a private key is lost, then bitcoin belonging to that key is unspendable.
If a seed phrase is partially lost or the user mixes up the order of a few words, it is possible to brute force all of the possible combinations. This carries significant risk, as downloaded programs can contain malware and people who offer help could take the bitcoin for themselves.
What Does Lost Bitcoin Mean For The Rest Of The Bitcoin Network?
Lost bitcoin increases the value of the remaining bitcoin on the network. Bitcoin is infinitely divisible, so lost bitcoin does not harm the network as a whole. Furthermore, because Bitcoin derives value from its absolutely finite supply, every lost bitcoin will slightly increase the value of the remaining bitcoin in the network.
How Can I Avoid Losing My Bitcoin?
Today, many protocols exist to safeguard private keys and passwords. Individual users who self-custody bitcoin are prone to human error and other unique threats. You can reduce the chance of losing your bitcoin by adhering to the latest standards in information security and data storage.
➤ Learn more about security measures for bitcoin storage.
Notice: River does not provide investment, financial, tax, or legal advice. The information provided is general and illustrative in nature and therefore is not intended to provide, and should not be relied on for, tax advice. We encourage you to consult the appropriate tax professional to understand your personal tax circumstances.Key Takeaways
- Nearly 4 million bitcoin are estimated to be lost forever.
- Each lost bitcoin increases the value of remaining bitcoin in the network.
- Many private keys held in self-storage are often accidentally discarded or overwritten by other files.
- The best way to avoid lost bitcoin is to safeguard private keys and verify the address of a counterparty before sending bitcoin to their address.


